Ear infection symptoms like a throbbing ear, muffled sound, or a strange fullness that won’t go away can signal a problem.
But is it really an ear infection, or could it be wax, allergies, or sinus congestion?
Ear infections are among the most common reasons people seek ear care in the UK.
They can range from mild discomfort to serious conditions that, if ignored, can spread to deeper structures.
In rare cases, an untreated inner ear infection may even lead to complications that affect balance or, very rarely, spread to the brain.
In this guide, we’ll break down the early symptoms of an ear infection, its different types, safe home care and treatment options, and when to visit Dewaxify for professional help.
What Exactly is an Ear Infection?
An ear infection happens when bacteria, viruses, or fungi invade any part of the ear, leading to inflammation, fluid build-up, and discomfort.
The type of symptoms you experience often depends on which part of the ear is affected.
Doctors typically classify ear infections into three main types:
- Outer Ear Infection (Otitis Externa):
Also known as “swimmer’s ear,” this infection affects the ear canal.
It’s often caused by trapped water, excessive moisture, or fungal growth.
Common signs include itching, redness, and pain, especially when touching the ear. - Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media):
This occurs when fluid builds up behind the eardrum, often after a cold, sinus infection, or allergies.
Symptoms can include ear pain, pressure, hearing difficulties, and sometimes fever. - Inner Ear Infection (Labyrinthitis):
A less common but more serious infection, labyrinthitis affects the deeper structures responsible for balance and hearing.
It can cause dizziness, vertigo, nausea, and temporary hearing loss.
Types of Ear Infections & Their Symptoms
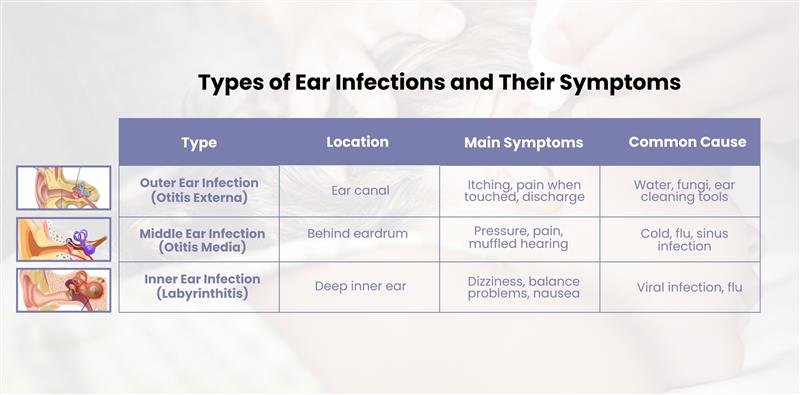
(source – MNT)
Early Signs and Symptoms of Ear Infection to Watch For
Recognizing the early signs of an ear infection is crucial because timely action can prevent the condition from worsening and speed up recovery.
Many ear infections start subtly, and the symptoms can vary depending on whether the infection is in the outer, middle, or inner ear.
Paying attention to these early warning signs can help you take the right steps whether that’s home care for mild cases or seeking medical attention for more serious infections.
Some common early symptoms to watch for include:
- Ear pain or pressure: A persistent ache or sharp discomfort in the ear.
- Feeling of fullness or blockage: The ear may feel “plugged” or heavy.
- Muffled or reduced hearing: Sounds may seem distant or quieter than usual.
- Itching or irritation: Often a sign of a fungal or outer ear infection.
- Fluid or discharge from the ear canal: Clear, cloudy, or even pus-like fluid may appear.
- Dizziness or imbalance: Usually linked to inner ear infections, causing vertigo or unsteadiness.
- Fever or fatigue: May accompany more severe infections.
If symptoms last more than 48 hours or are accompanied by dizziness and fever, it’s time to seek medical care.
Must Read>>>
How to Improve Ear Health: Simple Daily Habits, Expert Tips, and Natural Care Practices
What Causes Ear Infections?
Ear infections occur when bacteria, viruses, or fungi enter the ear and multiply, often thriving in the warm, moist environment of the ear canal or behind the eardrum.
While anyone can develop an ear infection, certain activities and conditions can increase the risk.
Common triggers include:
- Swimming or trapped water inside the ear
Frequent swimming or water getting trapped in the ear can create a damp environment that encourages bacterial or fungal growth.
This is why outer ear infections, often called “swimmer’s ear,” are so common. - Excess ear wax blocking airflow
While earwax protects the ear, too much of it can block airflow and trap bacteria, creating the perfect environment for an infection.
Blockages also make it harder for fluid to drain, which can lead to middle ear infections. - Allergies or sinus congestion after a cold
Allergies, colds, or sinus infections can cause fluid build-up and inflammation in the middle ear.
This trapped fluid can become infected, leading to pain, pressure, and hearing issues. - Scratching with cotton buds or sharp objects
Using cotton swabs, hairpins, or other sharp objects in the ear can scratch the delicate skin of the ear canal, making it more vulnerable to infection.
Such habits can also push wax deeper, causing blockages. - Using non-sterile earphones or hearing aids
Earphones and hearing aids can carry bacteria or fungi if not cleaned properly.
Repeated use without sterilization can introduce pathogens into the ear canal. - Poor immune health
People with weakened immunity are more susceptible to infections because their bodies may struggle to fight off invading bacteria or viruses.
This can make even minor irritations in the ear more likely to develop into an infection
Understanding these causes can help you take preventive measures like keeping ears dry, avoiding unnecessary scratching, and maintaining hygiene to reduce the risk of infections.
Fungal Ear Infection: A Common Yet Overlooked Cause
Fungal ear infections, medically known as otomycosis, are surprisingly common but often overlooked.
They thrive in warm and humid environments.
Prolonged exposure to moisture in the ear creates ideal conditions for fungi to grow.
Activities like swimming, frequent showering, or bathing in humid conditions can increase the risk.
Even antibiotic ear drops may trigger fungal infections by disturbing the ear’s natural microbial balance.
People with excessive earwax or minor ear canal injuries are also more vulnerable.
Symptoms to watch for include:
- Persistent itching inside the ear, often worsening over time.
- Discharge that can appear white, grey, or black.
- A musty or unpleasant odor coming from the ear.
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
- Mild hearing loss or muffled hearing due to blockage.
Left untreated, fungal ear infections can worsen, causing significant discomfort and, in rare cases, spreading deeper into the ear canal.
Fungal Ear Infection Treatment typically involves:
- Professional ear cleaning to remove debris and fungal buildup, often using microsuction.
- Antifungal ear drops prescribed by a clinician to eliminate the infection.
- Keeping the ear dry and avoiding swimming or inserting objects during treatment.
Prevention is also key.
Drying ears thoroughly after swimming or bathing, avoiding overuse of antibiotic drops, and maintaining ear hygiene can lower the risk significantly.
Home Remedies and Treatment for Ear Infections
Many mild ear infections improve on their own within a few days.
However, some infections need professional care depending on their type and severity.
Early intervention can prevent complications and reduce discomfort.
Safe Home Remedies for Mild Cases
- Warm Compress:
Applying a warm towel (never hot) over the affected ear can ease pain and reduce pressure.
The warmth increases blood flow and helps fluid drain naturally. Repeat for 10–15 minutes, several times a day.
This method is especially effective for middle ear infections and helps relax surrounding muscles. - Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter painkillers like paracetamol or ibuprofen can manage both ear pain and fever.
These medications reduce inflammation and make daily activities more comfortable.
Always follow the recommended dosage and avoid giving adult medications to children without guidance - Keep Ears Dry:
Moisture in the ear canal can worsen infections, particularly outer ear infections.
Avoid swimming, bathing in deep water, or inserting cotton swabs and other objects.
After showers, gently pat ears dry with a towel, but avoid pushing anything inside the canal. - Nasal Decongestants:
If the infection began after a cold or sinus congestion, nasal sprays or decongestants may help.
Reducing nasal swelling allows fluid behind the eardrum to drain more easily.
Always follow instructions carefully and limit use to avoid rebound congestion.
Avoid inserting oils, candles, or homemade solutions without professional advice.
Related Post>>>>
The Complete Guide to Ear Health: Expert Tips for Preventing Hearing Problems
Medical Treatment Options
If symptoms persist or worsen, professional treatment is essential.
- Bacterial Ear Infection: Treated with antibiotic ear drops or oral antibiotics.
- Fungal Ear Infection: Requires antifungal drops after ear cleaning.
- Severe Middle or Inner Ear Infection: May need prescription steroids or antivirals to reduce inflammation.
At Dewaxify, every patient undergoes an HD otoscopy to confirm whether symptoms are due to infection, wax blockage, or another issue.
Quick Relief vs Medical Treatment – What Works When
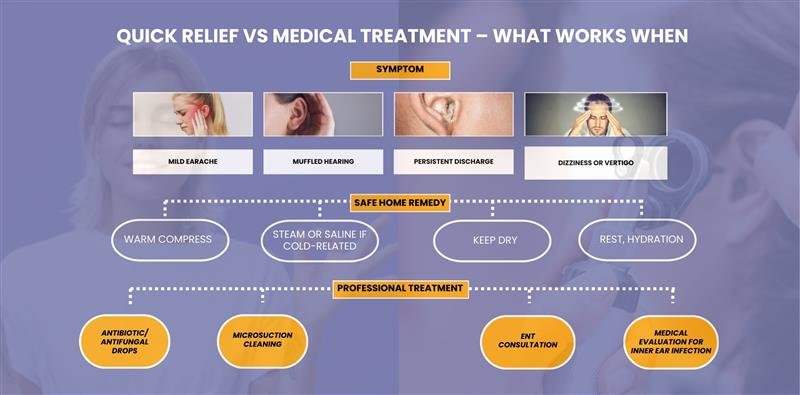
Can an Ear Infection Spread to the Brain?
It’s rare, but in severe untreated cases, especially chronic middle or inner ear infections, bacteria can spread beyond the ear.
Ear infection spread to brain symptoms can include:
- Severe headache or stiff neck
- Confusion or drowsiness
- High fever and persistent ear pain
- Vision or balance changes
While extremely uncommon, these symptoms require immediate medical attention.
If you ever experience these signs, go to an emergency department right away.
Most ear infections treated early at a clinic like Dewaxify resolve safely without complications.
Why Inner Ear Infections Need Prompt Care
The inner ear controls both hearing and balance. When inflammation affects this region, symptoms may include vertigo, nausea, or tinnitus.
Inner ear infections can be viral or bacterial and often need medication or ENT evaluation.
Delaying care increases the risk of lingering balance issues or nerve-related hearing loss.
7-Day Plan for Managing Ear Infection Symptoms Safely
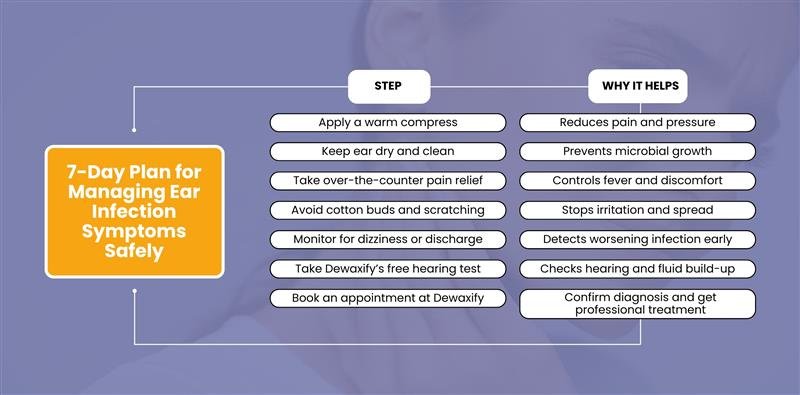
Dewaxify: London’s Trusted Ear Care and Infection Treatment Clinic
Dewaxify is a specialist ear clinic located in Ilford, East London, founded in April 2017 by Sita Parmar, a qualified Audiological Scientist.
Our clinic provides safe, accurate diagnosis and gentle ear treatments using state-of-the-art technology.
Services Include
- HD Otoscopy: High-definition examination to detect infection or wax.
- Microsuction Cleaning: Dry, gentle removal of debris and fungal build-up.
- Hearing Tests: Free online or in-clinic screening to assess hearing changes.
- Referral Pathways: Direct referrals to ENT specialists when needed.
Appointments start from £60 with free consultation and a hearing test.
For more details please visit our pricing page.
Ear Infection FAQs
What are the common ear infection symptoms?
Ear pain, fullness, muffled hearing, discharge, itching, and occasional dizziness.
How is an ear infection treated?
Treatment depends on the cause. Antibiotic or antifungal drops are common, along with professional ear cleaning.
What is a fungal ear infection?
A fungal infection in the ear canal causing itching, white or black discharge, and mild hearing loss.
Can an ear infection spread to the brain?
Very rarely. Severe untreated infections can cause complications. Ear infection spread to brain symptoms include fever, confusion, and severe headache.
How can I tell if it’s an inner ear infection?
Look for vertigo, balance problems, or nausea. These require prompt medical attention.












